Comunidades de morcegos (Chiroptera) do Parque Estadual do Rio Doce, um grande remanescente de Mata Atlântica no Sudeste Brasileiro
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35699/2675-5327.2007.23172Palavras-chave:
Atlantic forest, Minas Gerais, frugivory, Vismia magnoliifolia, Cecropia, bat reproduction, bioindicatorResumo
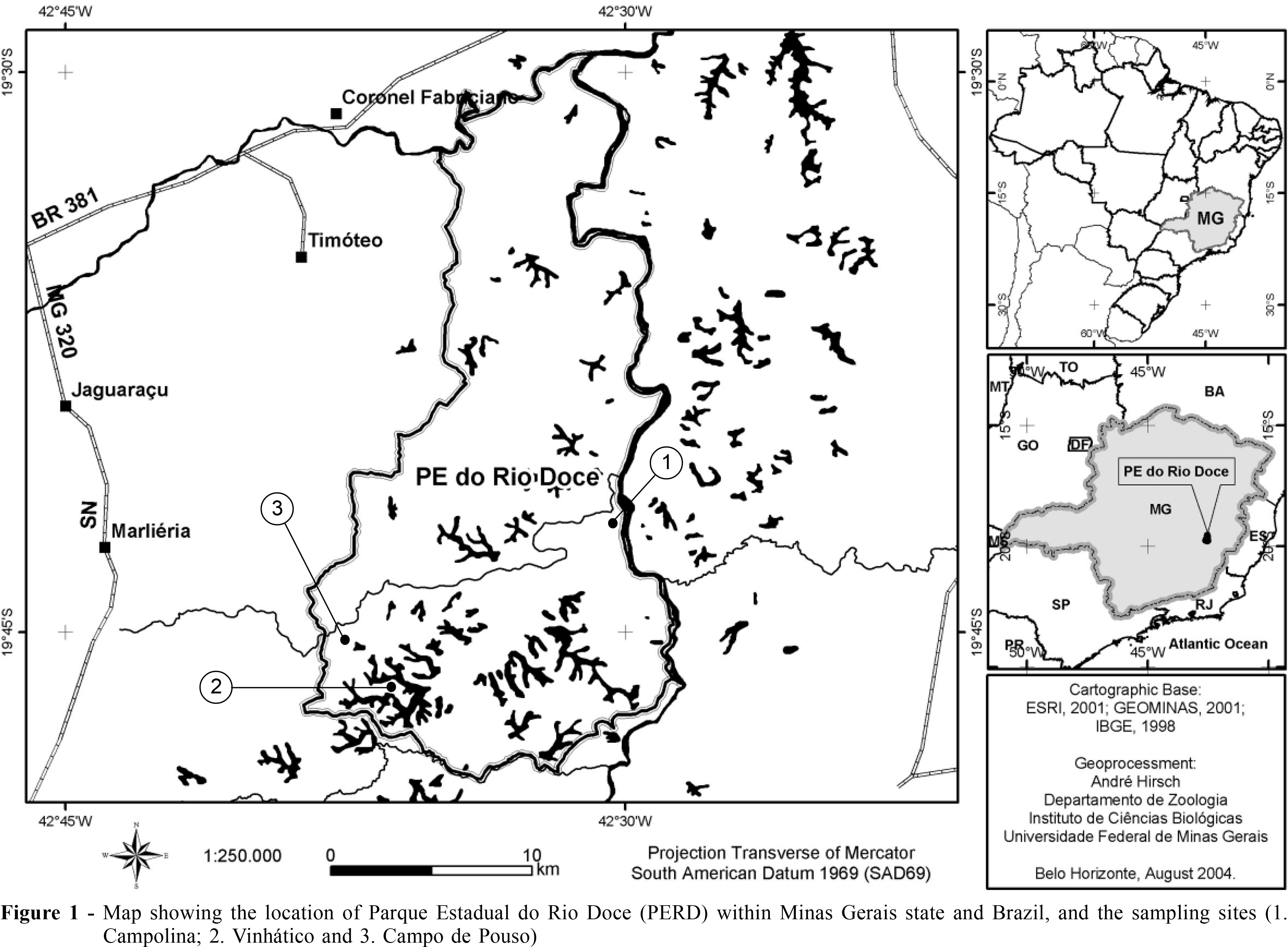
We surveyed the bat communities of a large Atlantic Forest reserve in the state of Minas Gerais, SE Brazil, the Parque Estadual do Rio Doce (PERD), over a period of ten months, collecting data on diet and reproduction of their bat species. We recorded bats using ground-level mist-nets erected in several environments within the park, and searched for bat roosts. Of a total of 33 species of bats recorded in the reserve to date, 24 bat species were recorded during this study,12 of which were first records for the park. Seeds of Cecropia predominated in the fecal samples of stenodermatine bats, and seeds of Piper were the main item in the fecal samples of Carollia perspicillata. We also got the first records of bats consuming fruits of Vismia magnoliifolia. Peaks of reproduction of bats in PERD occurred in the wet season, except for Desmodus rotundus, which was found reproductively active during the dry season. We suggest that the relative abundance of common species such as D. rotundus and Artibeus lituratus in the most disturbed areas within PERD may be correlated with distinct degrees of disturbance.
Downloads
Publicado
Edição
Seção
Licença

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
