Alien fishes in lakes of the Doce river basin (Brazil): range, new occurrences and conservation of native communities
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35699/2675-5327.2004.22015Keywords:
Alien species, biological invasions, biodiversity conservation, fish, tropical lakesAbstract
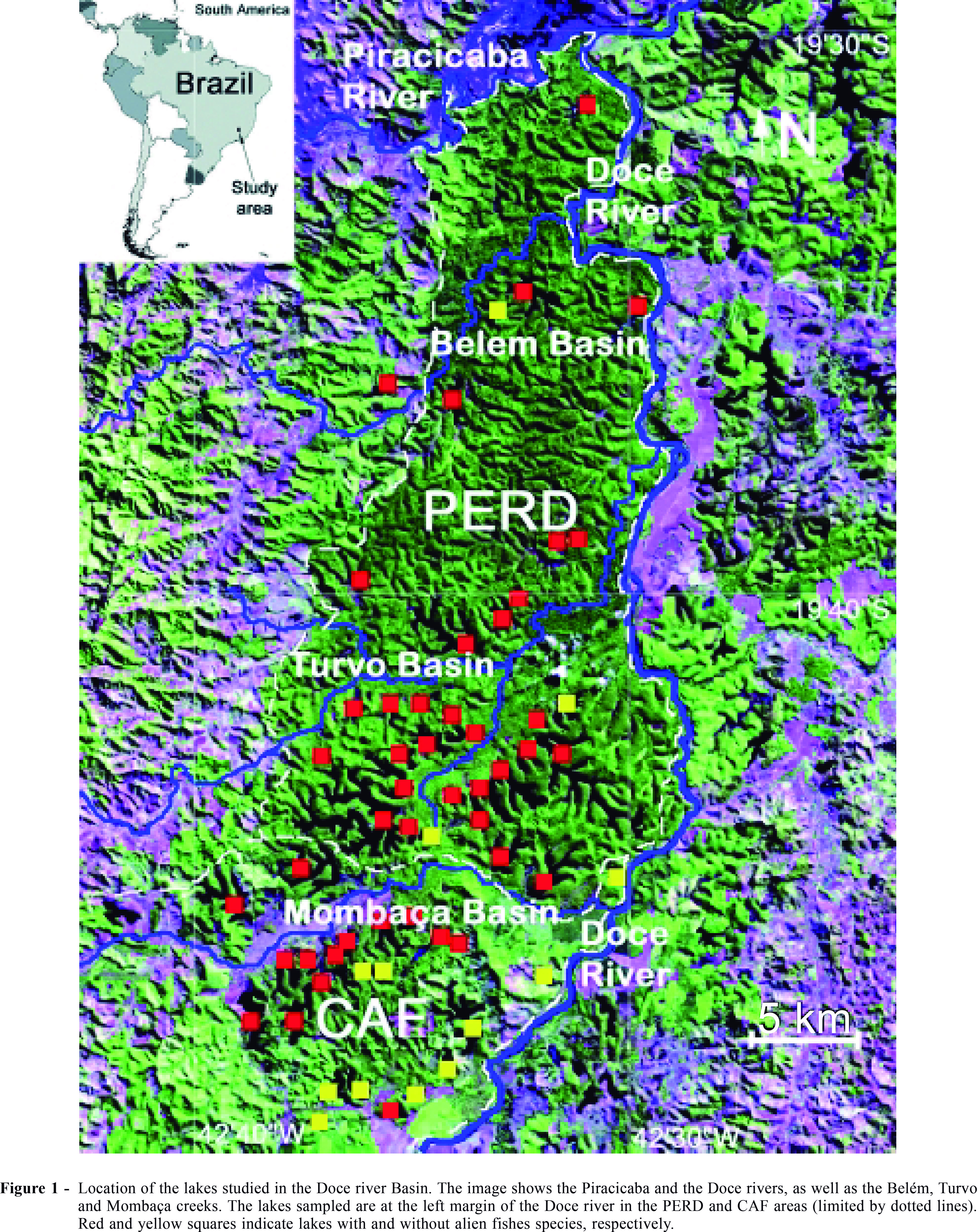
The present study shows the distribution of alien fish species in tropical lakes in the middle Doce river basin, southeastern Brazil, obtained from a rapid assessment program. The causes for their introductions were sportfishing improvement in some specific lakes and aquaculture in the studied basin. Presently, these species have a wide distribution occurring in 41 of the 54 lakes studied, representing an actual threat to regional native fish community. The natural connection among lakes and streams during the rainy season and the dispersal mediated by local people are the main invasion agents for alien fishes. The success of these invaders is probably due to absence of pre-existing effective competitors or top-predators in the invaded communities. We consider that the eradication of alien fishes by means of the available management tools may be very difficult due to the large number of lakes invaded and to the wide spectrum of lake conditions and resources exploited by these alien species. We recommend the use of environmental education as a tool to stop the human-mediated dispersion of aliens and to improve conservation of native fish community in lakes where these alien species are not present yet.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
